温馨提示:本文最后更新于
2024-12-12 18:19:44,某些文章具有时效性,若有错误或已失效,请在下方留言。单返回值
函数通过 return 关键字,进行函数的输出。
def function_name(input_parameter):
<body of function that uses input_argument>
return output
示例代码
def format_name(f_name, l_name):
f_name = f_name.title()
l_name = l_name.title()
# 函数输出
return f"{f_name} {l_name}"
title_name = format_name("my", "ran")
print(title_name)
多返回值
多个返回值可以是条件返回值,也可以是空返回值
# 条件返回值
def canBuyAlcohol(age):
if age >= 18:
return True
else:
return False
# 空返回值
def canBuyAlcohol(age):
# If the data type of the age input is not a int, then exit.
if type(age) != int:
return
if age >= 18:
return True
else:
return False
Docstrings
Docstring 文档字符串是由””” ””” 所包裹的内容,文档字符串会在
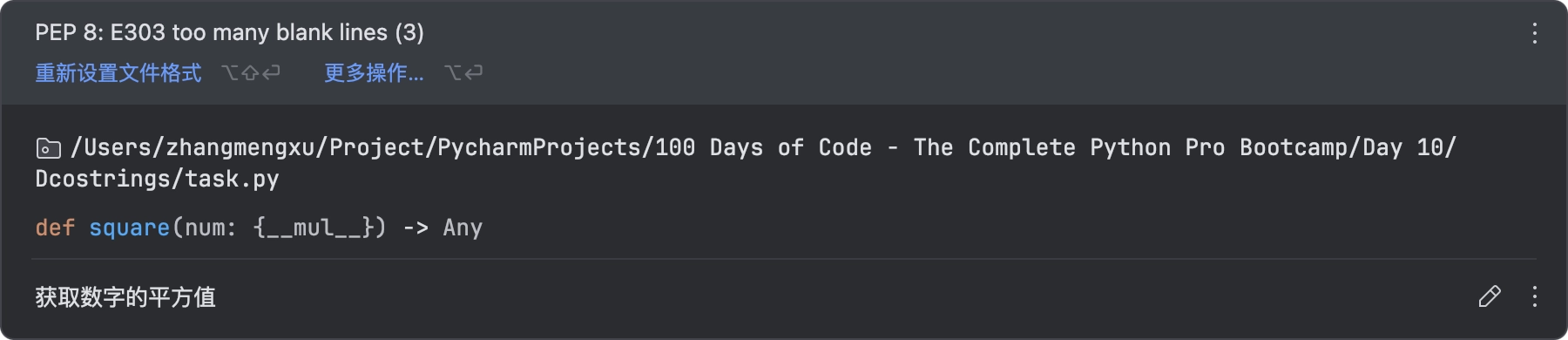
def square(num):
"""获取数字的平方值"""
return num * num
鼠标悬浮在函数上方,会显示文档字符串的内容
计算器项目
import art
def add(n1, n2):
"""加法运算"""
return n1 + n2
def subtract(n1, n2):
"""减法运算"""
return n1 - n2
def multiply(n1, n2):
"""乘法运算"""
return n1 * n2
def divide(n1, n2):
"""除法运算"""
return n1 / n2
# 函数名作为字典的值(value)
operations = {"+": add, "-": subtract, "*": multiply, "/": divide}
# 计算 4 * 8
# print(operations["*"](4, 8))
def calculator():
print(art.logo)
should_accumulate = True
num1 = float(input("What is the first number?: "))
while should_accumulate:
for symbol in operations:
print(symbol)
operation_symbol = input("Pick an operation: ")
num2 = float(input("What is the next number?: "))
answer = operations[operation_symbol](num1, num2)
print(f"{num1} {operation_symbol} {num2} = {answer}")
choice = input(f"Type 'y' to continue calculating with {answer}, or type 'n' to start a new calculation: ")
if choice == "y":
num1 = answer
else:
should_accumulate = False
print("\n" * 20)
calculator()
calculator()
© 版权声明
THE END






暂无评论内容