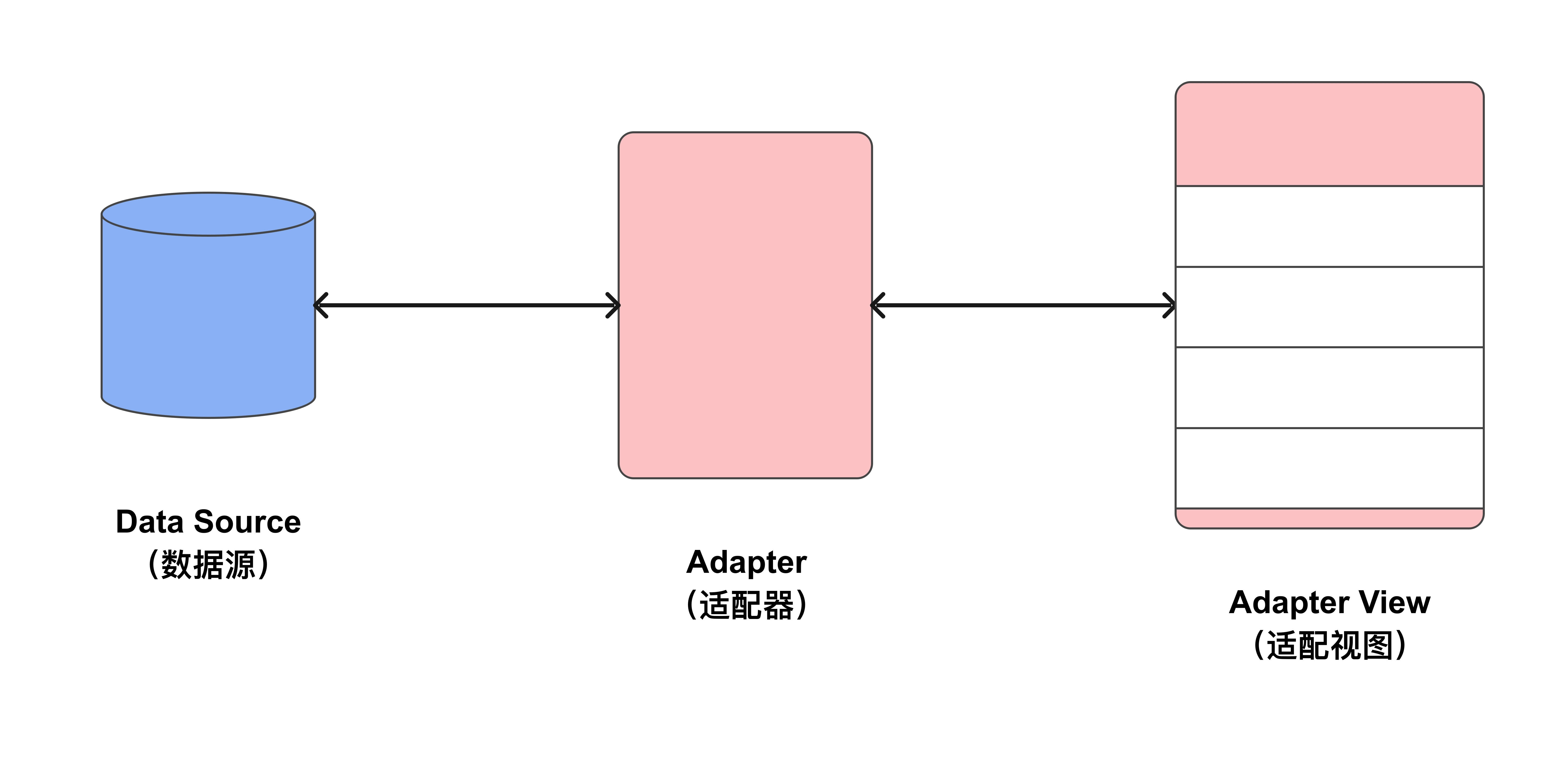
2025-11-24 09:28:10,某些文章具有时效性,若有错误或已失效,请在下方留言。Data Binding(数据绑定) 是一个支持库,它允许你在布局中使用声明式格式将 UI 组件绑定到应用中的数据源,而不是通过代码进行绑定。
数据绑定是将 XML 布局中的视图与数据对象进行整合的过程。Data Binding 负责生成此过程中所需的类。使用数据绑定时,系统会创建一个 binding 对象,其中包含对布局中每个视图的引用,因此 Android 系统不需要再通过视图 ID 一次次地去查找这些视图。
数据绑定基本使用
布局文件被 <layout></layout> 包裹,其名称是 activity_main。基于此,Android Data Binding 库将会创建一个名为 ActvityMainBinding 的绑定对象。
1. 开启数据绑定
在 build.gradle.kts Data Binding。
plugins {
alias(libs.plugins.android.application)
}
android {
namespace = "com.stewednoodles.databindingapp"
compileSdk {
version = release(36)
}
defaultConfig {
applicationId = "com.stewednoodles.databindingapp"
minSdk = 24
targetSdk = 36
versionCode = 1
versionName = "1.0"
testInstrumentationRunner = "androidx.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner"
}
buildTypes {
release {
isMinifyEnabled = false
proguardFiles(
getDefaultProguardFile("proguard-android-optimize.txt"),
"proguard-rules.pro"
)
}
}
compileOptions {
sourceCompatibility = JavaVersion.VERSION_11
targetCompatibility = JavaVersion.VERSION_11
}
// 1. 开启 data binding
buildFeatures {
dataBinding = true
}
}
dependencies {
implementation(libs.appcompat)
implementation(libs.material)
implementation(libs.activity)
implementation(libs.constraintlayout)
testImplementation(libs.junit)
androidTestImplementation(libs.ext.junit)
androidTestImplementation(libs.espresso.core)
}2. <layout> 标记
<layout></layout> 作为根元素,对布局文件进行标记。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!--2. <layout> 作为根元素进行标记-->
<layout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools">
<!--3. 数据绑定
- person 变量绑定 Person 类
- person 变量的使用方式 @{person.name}
-->
<data>
<variable
name="person"
type="com.stewednoodles.databindingapp.Person" />
</data>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout
android:id="@+id/main"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@{person.name}"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
</layout>3. 数据的绑定
使用<data>、<variable> 标签进行数据的绑定,下面的代码就是将变量 person 绑定到 Person 实例中。
<!--3. 数据绑定
- person 变量绑定 Person 类
- person 变量的使用方式 @{person.name}
-->
<data>
<variable
name="person"
type="com.stewednoodles.databindingapp.Person" />
</data>Person 文件的内容
package com.stewednoodles.databindingapp;
public class Person {
private String name;
private String email;
public Person(String name, String email) {
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public Person() {
}
}
4. 变量的使用
变量绑定之后,使用 @{} 对变量进行引用。
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@{person.name}"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />5. MainActivity
MainActivity 中的代码,如下所示
package com.stewednoodles.databindingapp;
import android.os.Bundle;
import androidx.activity.EdgeToEdge;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import androidx.core.graphics.Insets;
import androidx.core.view.ViewCompat;
import androidx.core.view.WindowInsetsCompat;
import androidx.databinding.DataBindingUtil;
import com.stewednoodles.databindingapp.databinding.ActivityMainBinding;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
//
private ActivityMainBinding binding;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
EdgeToEdge.enable(this);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(findViewById(R.id.main), (v, insets) -> {
Insets systemBars = insets.getInsets(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.systemBars());
v.setPadding(systemBars.left, systemBars.top, systemBars.right, systemBars.bottom);
return insets;
});
// 数据实例
Person person = new Person("Stewed Noodles", "stewednoodles.co@gmail.com");
// 绑定数据
binding = DataBindingUtil.setContentView(this, R.layout.activity_main);
binding.setPerson(person);
}
}6. 运行效果
最终的运行效果,如下图所示
![图片[1]-Data Binding 数据绑定-Stewed Noodles 资源](https://cdn.sa.net/2025/11/20/OjmQxVrdU1CiHbg.webp)
数据绑定事件处理
1. 创建事件处理类
添加事件处理类 MyClickHandler,代码内容如下所示
package com.stewednoodles.databindingapp;
import android.content.Context;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MyClickHandler {
Context mContext;
public MyClickHandler(Context mContext) {
this.mContext = mContext;
}
public void onButton1Click(View view) {
Toast.makeText(mContext, "First Button is clicked!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
2. 创建<data> 标签变量
在布局文件 activity_main.xml 文件的 <data> 标签中,引入 clickHandler 变量。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?><!--2. <layout> 作为根元素进行标记-->
<layout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools">
<!--3. 数据绑定
- person 变量绑定 Person 类
- person 变量的使用方式 @{person.name}
-->
<data>
<!--创建变量-->
<variable
name="person"
type="com.stewednoodles.databindingapp.Person" />
<!--创建方法变量-->
<variable
name="clickHandler"
type="com.stewednoodles.databindingapp.MyClickHandler" />
</data>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout
android:id="@+id/main"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@{person.name}"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<!--绑定按钮点击事件
- 使用 @{} 引入 方法变量 clickHandler
- 使用 :: 引入 方法
-->
<Button
android:onClick="@{clickHandler::onButton1Click}"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="128dp"
android:text="Click Me!"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
</layout>3. Button 绑定事件
绑定按钮点击事件,使用 @{} 引入 方法变量 clickHandler。变量 clickHandler 与方法名 onButton1Click 之间使用::。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?><!--2. <layout> 作为根元素进行标记-->
<layout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools">
<!--3. 数据绑定
- person 变量绑定 Person 类
- person 变量的使用方式 @{person.name}
-->
<data>
<!--创建变量-->
<variable
name="person"
type="com.stewednoodles.databindingapp.Person" />
<!--创建方法变量-->
<variable
name="clickHandler"
type="com.stewednoodles.databindingapp.MyClickHandler" />
</data>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout
android:id="@+id/main"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@{person.name}"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<!--绑定按钮点击事件
- 使用 @{} 引入 方法变量 clickHandler
- 使用 :: 引入 方法
-->
<Button
android:onClick="@{clickHandler::onButton1Click}"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="128dp"
android:text="Click Me!"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
</layout>4. Activity 绑定事件
在 MainActivity 中,绑定点击事件。
package com.stewednoodles.databindingapp;
import android.os.Bundle;
import androidx.activity.EdgeToEdge;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import androidx.core.graphics.Insets;
import androidx.core.view.ViewCompat;
import androidx.core.view.WindowInsetsCompat;
import androidx.databinding.DataBindingUtil;
import com.stewednoodles.databindingapp.databinding.ActivityMainBinding;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
//
private ActivityMainBinding binding;
private MyClickHandler clickHandler;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
EdgeToEdge.enable(this);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(findViewById(R.id.main), (v, insets) -> {
Insets systemBars = insets.getInsets(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.systemBars());
v.setPadding(systemBars.left, systemBars.top, systemBars.right, systemBars.bottom);
return insets;
});
// 数据实例
Person person = new Person("Stewed Noodles", "stewednoodles.co@gmail.com");
// 绑定数据
binding = DataBindingUtil.setContentView(this, R.layout.activity_main);
binding.setPerson(person);
// 绑定点击事件
clickHandler = new MyClickHandler(this);
binding.setClickHandler(clickHandler);
}
}5. 运行效果
运行效果,如下所示
双向绑定
BaseObservable 介绍
BaseObservable 是 Android Data Binding 提供的一个基类,让普通的 Java/Kotlin 对象具备“可观察”能力。
当对象的属性改变时,可以调用 notifyPropertyChanged() 来通知 UI 更新,无需手动 setTex() 或刷新界面。使用于
- MVVM 中的 Model
- 表单双向绑定
- 需要自动刷新 UI 的 POJO 数据类
使用步骤
1. Model 继承 BaseObservable
public class User extends BaseObservable {
private String name;
@Bindable
public String getName() { return name; }
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
notifyPropertyChanged(BR.name);
}
}2. 布局中绑定
<layout>
<data>
<variable
name="user"
type="com.example.User" />
</data>
<TextView
android:text="@{user.name}" />
<EditText
android:text="@={user.name}" /> <!-- 双向绑定 -->
</layout>注意:布局文件中双向绑定中使用的是 @={}。
示例代码
模型类 Person 的内容,如下所示
package com.stewednoodles.databindingapp;
import androidx.databinding.BaseObservable;
import androidx.databinding.Bindable;
//
public class Person extends BaseObservable {
private String name;
private String email;
public Person(String name, String email) {
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
}
@Bindable
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
notifyPropertyChanged(BR.name);
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public Person() {
}
}
布局文件的内容,如下所示
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?><!--2. <layout> 作为根元素进行标记-->
<layout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools">
<!--3. 数据绑定
- person 变量绑定 Person 类
- person 变量的使用方式 @{person.name}
-->
<data>
<!--创建变量-->
<variable
name="person"
type="com.stewednoodles.databindingapp.Person" />
<!--创建方法变量-->
<variable
name="clickHandler"
type="com.stewednoodles.databindingapp.MyClickHandler" />
</data>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout
android:id="@+id/main"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@{person.name}"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<!--绑定按钮点击事件
- 使用 @{} 引入 方法变量 clickHandler
- 使用 :: 引入 方法
-->
<Button
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="128dp"
android:onClick="@{clickHandler::onButton1Click}"
android:text="Click Me!"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text_view2"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginBottom="189dp"
android:text="@{person.name}"
android:textSize="32sp"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" />
<EditText
android:text="@={person.name}"
android:id="@+id/edit_text"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginBottom="104dp"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
</layout>最终的运行效果,如下所示









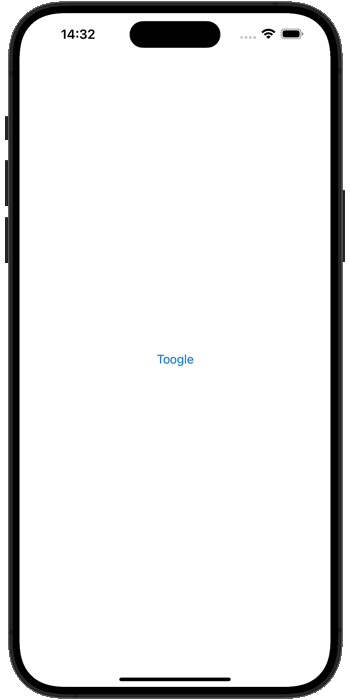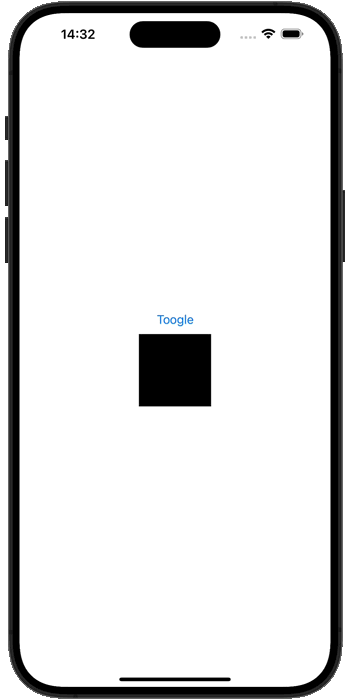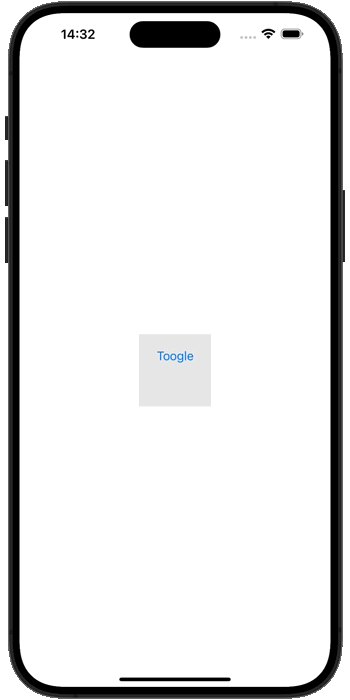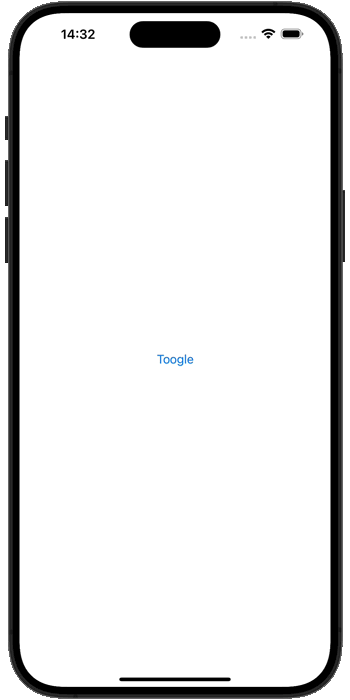

暂无评论内容